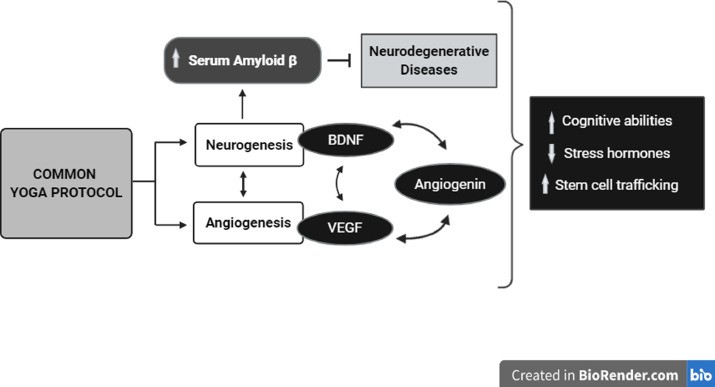
Abstract
Objective
To examine the molecular effects of mindful activities such as yoga and meditation
Design
This was an open label single arm exploratory yoga intervention study.
Study participants
64 healthy individuals within the age of 18–60 years were recruited for this one month yoga intervention study.
Intervention
Common Yoga Protocol (CYP) is a standardized yoga protocol released by Ministry of AYUSH, India for International Yoga Day. It includes all aspects of yoga i.e. asanas, pranayama and meditation. It is designed for adoption by all age groups for the health of community.
Outcome measures
The participants were assessed for biochemical parameters including Fasting Sugar and Lipid profile. The molecular markers of neurogenesis (i.e. Brain derived Neurotropic Factor, BDNF) and Angiogenesis (i.e. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, VEGF and Angiogenin) along with Amyloid β (marker related to neuro-degenerative diseases) were assessed. All the assessments were made at baseline and after one month of the intervention.
Results
After one month of CYP practice High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) levels increased significantly (p<0.001), although other biochemical parameters i.e. fasting sugar and other lipid assessments were found to be unaltered. Angiogenesis marker, angiogenin was increased significantly (p<0.002), other angiogenesis marker VEGF did not show any change along with BDNF, marker of neurogenesis. Amyloid β levels were also unaltered. Even though individual levels of VEGF and Amyloid β did not show any change, proportion of VEGF to Amyloid β showed a significant increase (p<0.001) after one month of CYP intervention indicating that the change in VEGF levels was significantly higher than the change in Amyloid β levels.
Conclusion
CYP practice may influence cell survival pathways mediated by angiogenic and neurogenic cross talk. Hence, CYP can be considered as a preventive measure for diseases associated with impaired angiogenic and neurogenic mechanism. This is the first study to examine the effects of CYP at the molecular level.